Embedding
B.Sc course, University of Debrecen, Department of Data Science and Visualization, 2024

Word embeddings are dense vector representations of words in a continuous vector space, typically learned from large text corpora using techniques like Word2Vec, GloVe, or FastText. These embeddings capture semantic and syntactic similarities between words, enabling algorithms to understand and process natural language more effectively.
Here’s how the process of “embedding tokenization” might work:
- Tokenization: The input text is tokenized into individual words or subword units using a tokenization technique such as word-level tokenization, subword tokenization (e.g., Byte-Pair Encoding), or character-level tokenization.
- Word Embedding Generation: Each token (word or subword) is mapped to its corresponding word embedding vector in a pre-trained embedding space. This mapping is based on a learned embedding model trained on a large corpus of text data. The embedding vectors capture semantic and syntactic relationships between words, such that similar words have similar vector representations.
- Representation: The resulting embedding vectors form a dense representation of the input text, where each token is represented by a high-dimensional vector in the embedding space. These embeddings can then be used as features for downstream NLP tasks, such as text classification, sentiment analysis, or machine translation.
Embedding tokenization, as described above, combines tokenization with the generation of word embeddings to represent text data in a continuous vector space. This approach allows for capturing semantic meaning and contextual information from the text, enabling more sophisticated and accurate NLP models and applications.
GLoVE
GloVe (Global Vectors for Word Representation) is an embedding technique used as a word embedding method in the field of natural language processing. GloVe is a distribution-based method that uses co-occurrence probabilities to determine relationships between words and create word embeddings.
GloVe essentially seeks to turn individual words into vectors that represent the relationships between words and their semantic meaning. The algorithm takes into account how common or rare each word is and how often it occurs together with other words. Accordingly, it tries to optimize the word vectors to reflect these occurrence patterns.
How to work?
- Creating a co-occurrence matrix: First, we create a so-called co-occurrence matrix from a large text corpus. co-occurrence matrix, which records which words occur together and how often in the text.
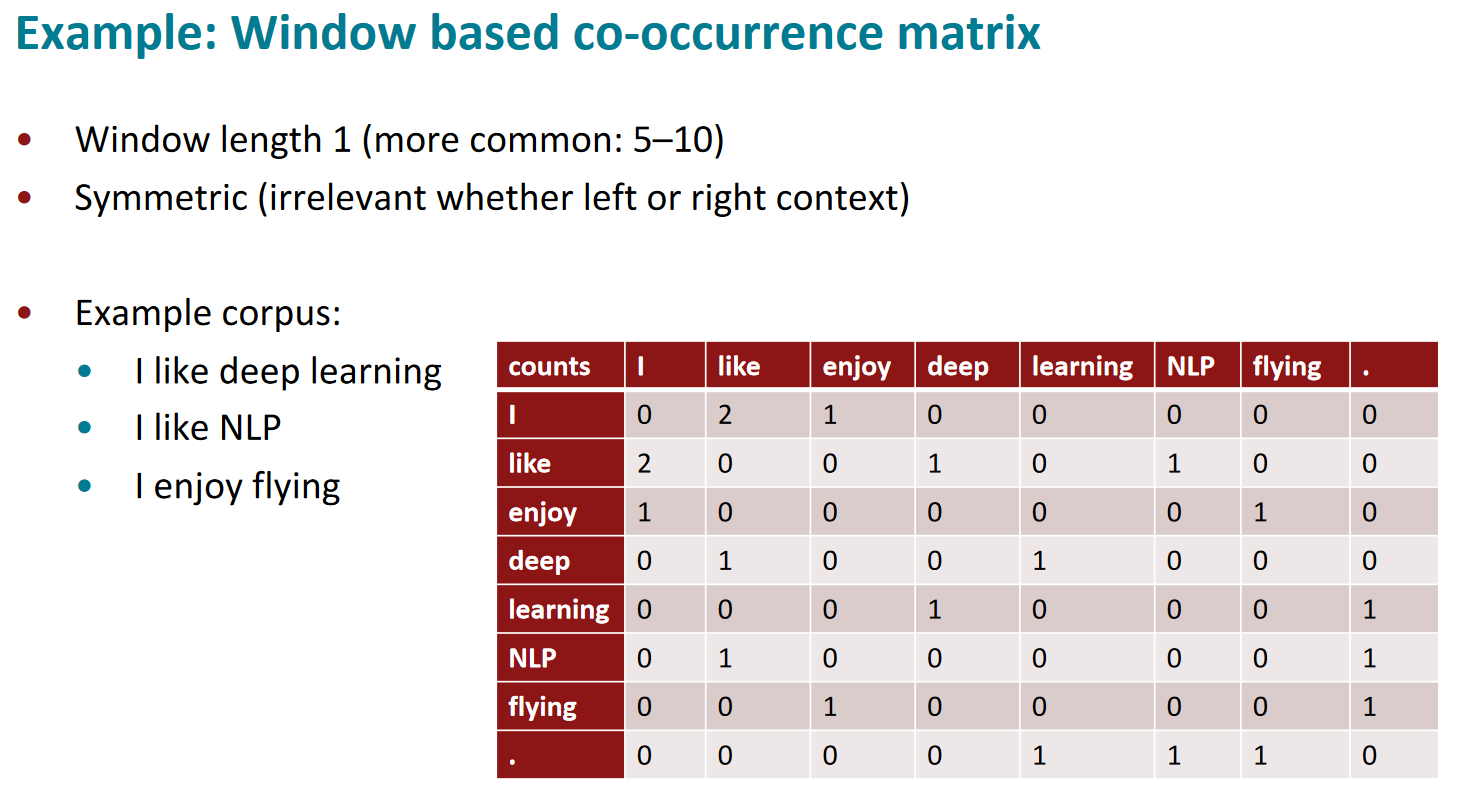
- Dimension size reduction. (Singular Value Decomposition of co-occurrence matrix X)
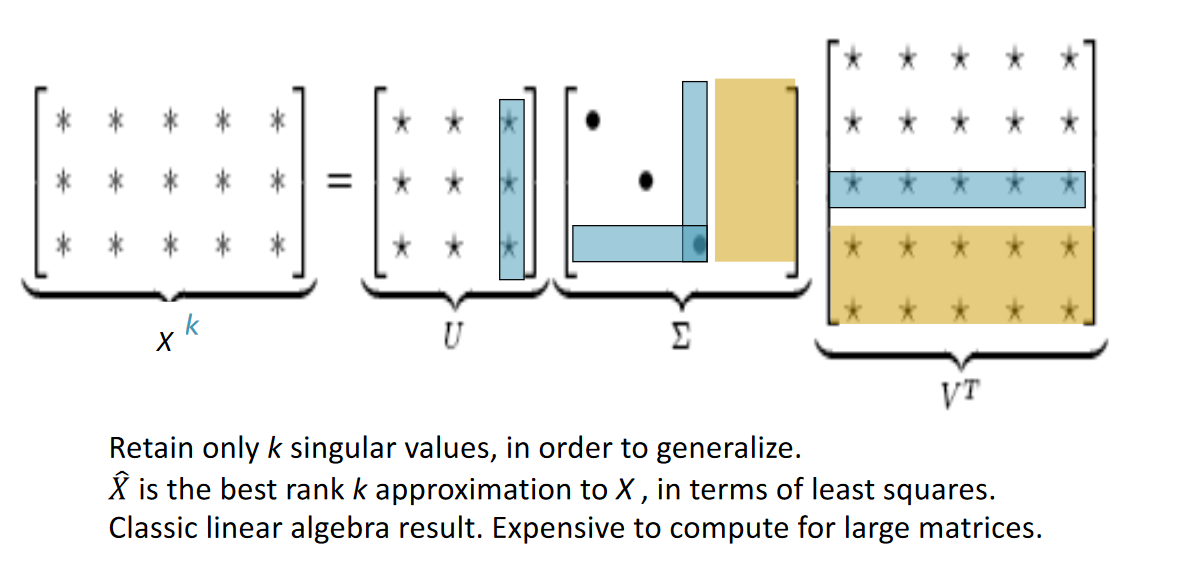
- Structure Optimization: The goal is to create word vectors that allow the best description of the corpus statistics. During the optimization process, GloVe weights the frequency of each word and the relationships between them.
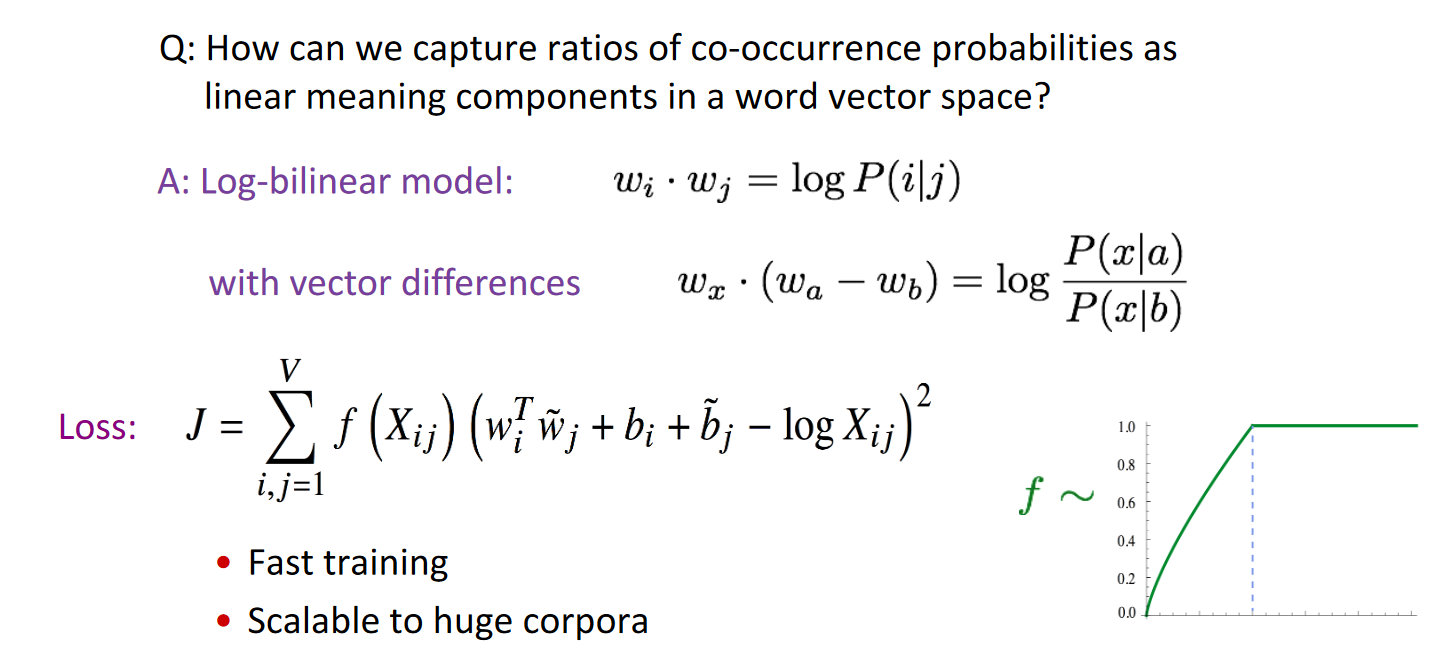
- Computation of word vectors: GloVe finally generates vectors that it assigns to words in the corpus. These vectors express semantic relations and structures between words.
- Related to general evaluation in NLP: Intrinsic vs. extrinsic
- Intrinsic:
- Evaluation on a specific/intermediate subtask
- Fast to compute
- Helps to understand that system
- Not clear if really helpful unless correlation to real task is established
- Extrinsic:
- Evaluation on a real task
- Can take a long time to compute accuracy
- Unclear if the subsystem is the problem or its interaction or other subsystems
- If replacing exactly one subsystem with another improves accuracy à Winning!
Word2Vec
Word2vec (Mikolov et al. 2013) is a framework for learning word vectors
Idea: - We have a large corpus (“body”) of text: a long list of words - Every word in a fixed vocabulary is represented by a vector - Go through each position t in the text, which has a center word c and context (“outside”) words o - Use the similarity of the word vectors for c and o to calculate the probability of o given c (or vice versa) - Keep adjusting the word vectors to maximize this probability
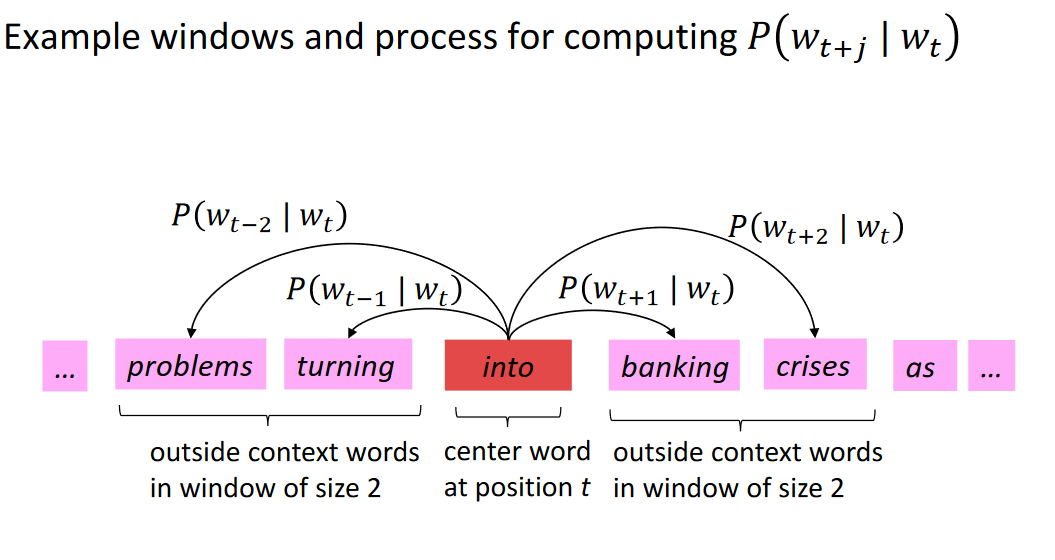
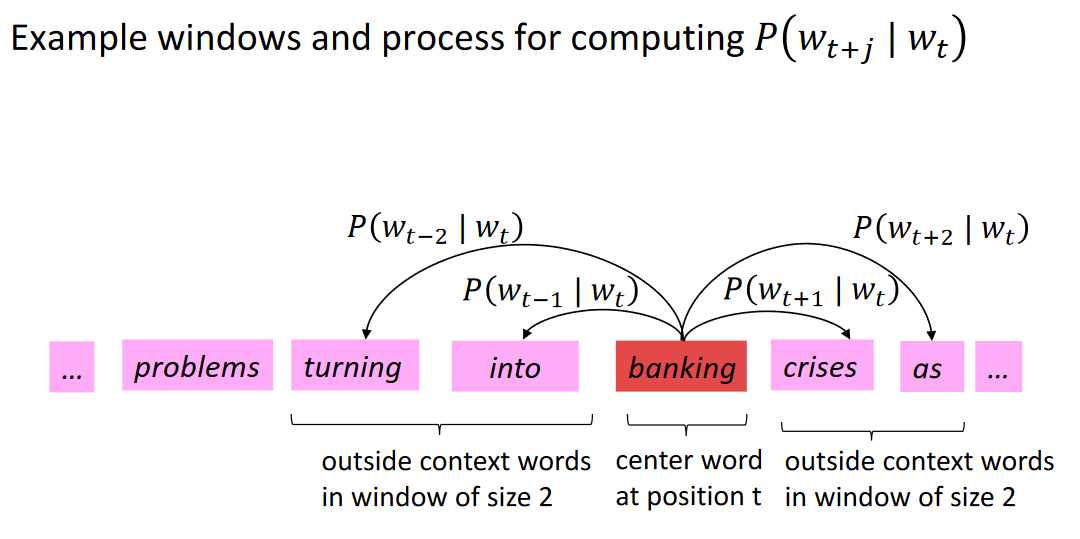
CBOW, Skip-gramm
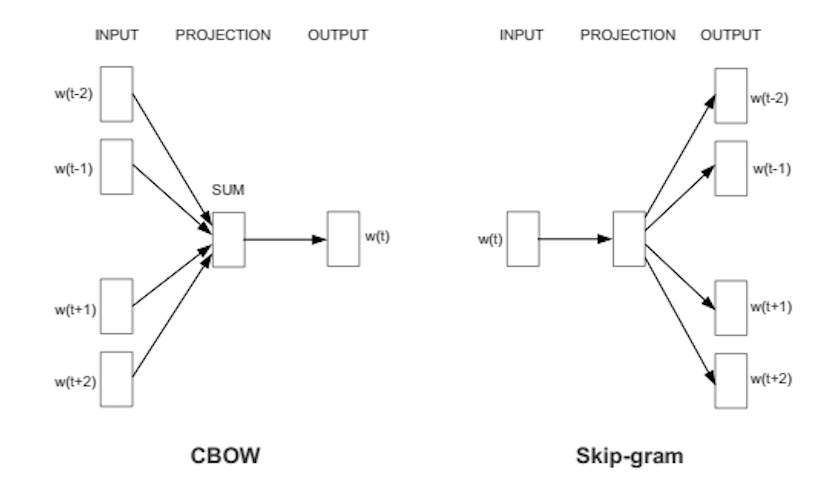
Ábra 3: CBOW, Skip-gramm. Forrás: wiki.pathmind.com.
Word2Vec CBOW

Ábra 4: Word2Vec CBOW. Forrás: medium.
